Solar PV (photo voltaic) panel price drastically dropped in the last couple of years and also encouraging government policies pulled the people to look into the solar Inverter as an option for their home power.
In market there are many PV panel and inverter manufacturers with different technologies confuses a common man. Here we are providing a brief explanation along with positives and negatives.
Types of Solar PV panels:
There are mainly three types of solar panels available at market. These are explained below:
Mono-crystalline silicon:
As the name suggests mono crystalline silicon panels made from a single continuous crystal structure. These are in dark black color. This is most expensive technology but it’s also the most efficient sunlight conversion. Module efficiency is around 15-20%.
Mono-crystalline silicon
Positives:
- High efficiency compared to all other types.
- Better life span. Most of the manufacturers gives 25-year warranty.
- These panels are space-efficient.
- These are more efficient in warm weather.
Negatives:
- Most expensive compared to all other types.
Poly (Multi)-crystalline silicon:
As the name suggest these type of panels use multi crystalline Silicon. Bluish shade distinguish poly crystalline panels from mono crystalline panels, these are in dark blue color.These are slightly less efficient compared to Mono-crystalline silicon modules. Module efficiency is around 13-16%.

Poly (Multi)-crystalline silicon
Positives:
- These are comparatively cheaper than others.
- Good life span. Most of the manufacturers gives 25-year warranty.
Negatives:
- Not space effective compared to mono-crystalline PV cells..
- slightly lower heat tolerance than mono-crystalline solar panels so perform slightly worse than mono-crystalline PV cells.
Thin-Film Solar Cells:
Silicon material is vaporized and deposited on glass or stainless steel. The cost is lower than any other technology. Module efficiency is around 7-13%. Most common photo-voltaic substances used are:
- Amorphous Silicon
- Cadmium Telluride (CdTe)
- Copper indium gallium selenide (CGIS)
- Dye-sensitized solar cell (DSC)

Thin-Film Solar Cells
Positives:
- Significantly higher temperature resistance compared to crystalline-based solar panels.
- These modules are flexible so these will fit at curved surfaces.
- Better resistance against shading.
Negatives:
- Lower efficiency.
- For the same power production these consumes more space compared to all other technology modules.
- Fast degrading.
How to size Solar Panel for Power Requirement:
To size the solar panel, first you need to decide whether all your loads are powered by solar panels or partial loads are powered by solar panels. If you want all your loads are powered by solar panels, one of the easiest-way to calculate the power requirement is from your average power bill. For example:
Average monthly usage = 175 units
Daily usage = 175/30 = 5.83 units = 5.83 KWh (1 unit = 1 KWh)
Average Sun light hours per a day = 5 hours
Lets consider efficiency of system (Panel wires, junction box, battery & Inverter losses) = 80%
Solar panel size = 5.83/(5 * 0.8) = 1.45 KW
So 1.5 KW solar panel will fit to your load requirement.
If you want only your partial loads are powered by solar panels, then calculate power requirement by using below link.
https://www.shoutforlatest.com/how-to-choose-right-house-hold-inverter/
Suppose power requirement = 770 watt
Solar panel size = 770/(0.8) = 962 watt
So 1 KW solar panel will fit to your load requirement.
Normally all solar panels below 100 watt rating comes with output voltage of 12v and more than 100 watt comes with 24v. So to meet your power requirement you have to choose parallel and series combination of panels. And also keep in mind if you want use existing inverter battery then chose panel voltage rating accordingly.
For 1.45 KW power requirement you need to choose six numbers of 250 watt panels, mostly these are comes with 24v output.
For 770 watt power requirement you need to choose 8 numbers of 100 watt panels, mostly these are comes with 12v output.
In general to setup 1000 watt PV panel system typically requires 10 square meters. Solar panel typical costs are:
mono crystalline – 60 to 70 Rs / watt.
Poly crystalline – 50 to 60 Rs / watt.
How to select Solar Inverter:
Unlike normal inverters solar inverters comes with charge controller. If solar power available the solar inverters charge the battery from solar panel, if solar power not available,then the inverter charges the battery from mains. If insufficient power available then mainly these inverters gives priority to charge the battery and the remaining power supplies to loads. There are mainly two types of inverter technologies available:
- MPPT (Maximum Power Point tracker) control
- PWM (Pulse width Modulation) control
MPPT based solar inverters are 30% efficient than PWM based inverters but these are costlier than PWM inverters. It is recommended to choose MPPT based solar inverter.
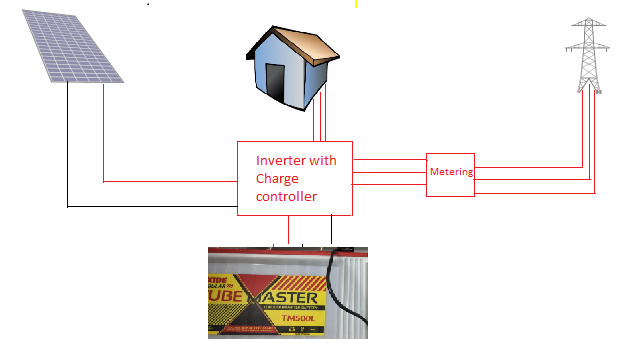
Solar Inverter
Inverter Rating:
For 1.5 KW solar panel inverter rating = 1.5/0.7 (power factor) = 2.07 KVA
So 2 KVA rated inverter will works for you power load.
How to size a battery:
Choosing a right battery is very important. Inverter performance entirely depends on it. Battery size depends on the how many hours of backup you need.
Let’s consider backup time of 4 hours. And we know 24V output comes from PV panel.
Battery Capacity = 1450 * 4 / 24 = 241.6 Ah
But all inverters comes with 80% efficiency only.
So final rating of your battery = 241.6 + 241.6*0.2 = 289.9 Ah
So finally 300 Ah battery will fit for your power requirement.
How to get subsidy from government:
If you are at INDIA you may get subsidy from Central Govt and State Govt. This is around 30% of the total investment as Central Govt subsidy. First you have choose the right supplier from whom you purchase the Solar PV system. The supplier should be approved by MNRE (Ministry of New and Renewable Energy). Please check the below link for list of suppliers which are approved by MNRE.
http://www.mnre.gov.in/information/manufacturesindustriesarchitectsconsulting-organisation/

